Introduction to Apache Airflow: Workflow Automation with DAGs and Tasks
In today’s technological landscape, process automation has become a fundamental component for improving the efficiency and productivity of organizations. In this introductory conference on Apache Airflow, we will explore how to use DAGs (Directed Acyclic Graphs) together with tasks to orchestrate and automate workflows effectively.
During the session, we will delve into the concept of DAGs and how to use them to define workflows, organizing tasks into a logical and sequential flow. We will also explore the role of tasks within DAGs, explaining how they represent individual units of work and how they can be configured to perform specific actions, such as data processing, script execution, or notification sending.
We will also explore how Airflow simplifies the programming and execution of tasks, offering a wide range of predefined operators and the flexibility to create custom operators to meet the specific needs of the workflow. We will demonstrate how to define tasks within a DAG, schedule them, and monitor them to ensure reliable and smooth execution.
Lecture by Dr. M. Palese.
Uploaded by Aristotle University of Thessaloniki.
Introduction to Kubernetes
Lecture by Prof. Lorentzo Carnevale.
Uploaded by Aristotle University of Thessaloniki.
Introduction to Containers with Docker
Lecture by Prof. Lorentzo Carnevale.
Uploaded by Aristotle University of Thessaloniki.
Introduction to Cloud/edge computing
Cloud Computing during the time has gained concrete evidence to be a disruptive technology still in its full development. Many drawbacks of the Cloud have brought to improve many their crucial aspects, like performance, security and privacy, etc. Today Edge Computing try to deal with these implications to make them less problematic and much more feasible. Starting from the NIST definition (IaaS, PaaS and SaaS), the talk looks at the last decade of ICT evolution preparing the systems for new ICT challenges and implementations, like AI algorithms on top of them.
Lecture by Prof. Lorentzo Carnevale.
Uploaded by Aristotle University of Thessaloniki.
Attention and Transformers Networks in Computer Vision Lecture
Abstract
This lecture explores various transformer-based approaches that have emerged as powerful alternatives of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in Computer Vision, and revolutionized the way visual information is analyzed. While CNNs have been the dominant architecture for visual tasks, they face challenges in capturing long-range dependencies and handling variable-sized inputs. Recent research has shown promising results by combining convolutional layers with attention mechanisms. Specifically, attention mechanisms allow the model to focus on relevant regions of the image, enabling better contextual understanding.
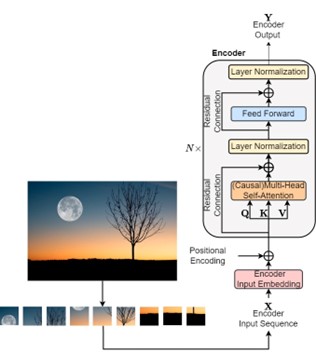
Specific transformer architectures designed for computer vision tasks are introduced, including the Vision Transformer (VIT), which replaces the traditional convolutional layers with self-attention mechanisms, facilitating better global information integration. Furthermore, the Detection Transformer (DETR) introduces transformers to object detection, achieving impressive results by utilizing a set-based representation of objects. Similarly, the Segmentation Transformer (SETR) and Segment Anything Model (SAM) leverage transformer architectures for semantic segmentation tasks, demonstrating improved performance in capturing fine-grained details. The lecture also explores unsupervised transformers such as the self-distilling DinO, which leverage self-supervision to learn representations without the need for explicit labels. Finally, the Video Vision Transformer (ViViT) extends the transformer architecture to video understanding, capturing spatiotemporal dependencies and achieving state-of-the-art performance. Several applications are presented, notably in industrial surveillance (pipeline image segmentation and pipeline detection) as well as in natural disaster management (e.g., forest fire detection, detection of flooded houses).
Figure: Typical Vision Transformer architecture.
Lecture by N. M. Militsis and Prof. Ioannis Pitas
Link to the video.
AI University Education
This lecture overviews the impact of AI on education. First of all, the impact of AI on citizen education at High School level is overviewed. Then, the following question is debated: Is AI Science and Engineering a separate scientific discipline? The extend and geographical distribution of the AI studies worldwide is presented. Furthermore, the impact of AI in teaching various other scientific disciplines at University level is analyzed. Finally, the LLM (e.g., ChatGPT) implications on education are also overviewed, notably its capabilities to reply exam questions, including mathematical and programming ones.